|
| |||
|
ANNOUNCEMENTS &
NEW ITEMS:
Meanwhile, mankind’s enslavement continues. It
works like this: In order to get people to accept a fully-surveilled, open
prison, cashless society, social credit system, ... a gradual wearing down
process is implemented. “First you wear people down. Poison them with drugs,
vaccines, fluoride, and chemical assaults so they become fat and dumb. Put
addictive devices in their hands and bombard them with propagandized movies,
TV, and Masonically-controlled actors and musicians. Destroy the food
supply, poison the water and the air, manufacture fake climate change while
blaming it all on the people, and tax them to death for it.” Push
‘sustainability’ according to the UN-2030 Agenda and the
World-Economic-Forum Cult. Work towards the implementation of “15-minute
SMART-city enslavement camps.” At the same time “give them all sorts of
distractions, from the two-party political charade (with the illusion of
choice when it is a totally rigged game), manufacture social disharmony, and
grow up controlled opposition to divide and conquer any truth movement that
appears to be gaining any momentum.”
Meanwhile: We stand at a crisis—the supreme crisis of the ages. For unnumbered millenniums man has toiled upward from the dank jungles of savagery toward glorious heights which his mental and spiritual potentialities give promise that he shall attain. His path has been slow and wavering. Time and again he has lost his way and plunged into deep valleys. Man’s trail is littered with the wrecks of dead civilizations and dotted with the graves of promising peoples stricken by an untimely end. –Lothrop Stoddard’s dire warning of the dangers of the practice of dysgenics (1921 !)
The World Conquerors, The Real War Criminals by Louis Marschalko
Meanwhile: Reflect on the mega-crime of the last century —Dresden
Hellstorm (February 13-15, 1945). It is appalling to think its
perpetrators were actually hailed as war heroes!
| |||
|
“Laws of Physics Twentieth-Century Scientists
Overlooked”
Available on AMAZON.com
The Nature of Gravitational Collapse
Guide to the Construction of the Natural Universe
Participate in a unique exploration of the Cosmos: venture into the
sub-atomic realm, even into the sub-quantum realm where the roots of reality
reside, and into the domain of cosmic-scale cell-structure and beyond to
infinity. Along the way, discover the cause of mass, the cause of
gravitation, and rediscover Einstein’s “nonponderable” aether and Heraclitus’
harmony-of-opposites principle. … The book represents the ultimate
vindication for all the skeptics who resisted the "preposterous" Big Bang
mythology and who refused to join the exploding-cosmos religion. POPULAR RESEARCH PAPERS:
| |||
|
Glossary of Terms
used in Cosmology and Astrophysics with particular emphasis on DSSU theory. |
|||
|
GENERAL INTEREST ARTICLES: | |||
|
COSMOLOGY ARTICLES, etc:
Large-Scale Structure of the Dynamic Steady State Universe published in
the American Journal of Astronomy and Astrophysics, Vol.4, No.6,
2016, pp.65-77.
Astract and Links. Galaxy Morphology:
Ellipticity, Its Origin & Progression in Comoving Galaxies, American Journal of Astronomy & Astrophysics,
AJAA, Vol.3, No.2, 2015.
EXTERNAL LINKS:
| |||
|
DSSU Theory:
The Fundamental Process of Energy —A Qualitative Unification of
Energy, Mass, and Gravity. (Abstract
& Reviews & Links) … This article reveals
the secret behind photon confinement. (Contains only a bare minimum of mathematics
and mainly in one of the 14 sections.)
Headlined as:
| |||
|
ARTICLES on AETHER: |
|||
|
DSSU RESEARCH PAPERS: |
|||
|
GRAVITY:
|
|||
|
RELATIVITY ARTICLES: |
|||
|
An Open Letter to the Scientific Community "The big bang today relies on a growing number of hypothetical entities, things that we have never observed-- inflation, dark matter and dark energy are the most prominent examples. Without them, there would be a fatal contradiction between the observations made by astronomers and the predictions of the big bang theory. In no other field of physics would this continual recourse to new hypothetical objects be accepted as a way of bridging the gap between theory and observation. It would, at the least, raise serious questions about the validity of the underlying theory. ..." continues ... A devastating Declaration of opposition to Big Bang cosmology signed by more than 400 Researchers.
|
|||
|
INTELLECTUAL FREEDOM:
|
|||
|
DEDICATION: This website is solemnly dedicated to those
individuals who have conducted research in their chosen field and have
informed others of their inquiries and suffered the consequences when
subpoenaed by the Inquisition or some variant thereof. The dedication
extends to those individuals currently imprisoned, and those facing
trial and persecution simply for exercising their basic human right of
freedom of expression supposedly granted to them under the UN Charter of
Human Rights. "Every year, hundreds of writers and other literary professionals around the world are imprisoned, prosecuted, persecuted, attacked, threatened, forced into exile or even murdered as a result of their work." ALSO: Be aware of the continuing threat to our precious freedom of expression on the Internet. The threat is serious and relentless. It is described as “… the formal effort to mimic Communist China’s system of Internet censorship.” – www.InfoWars.com More information on threats to internet freedom: https://battleforthenet.com/ End of free speech in Britain:
A publisher of history books in Britain has reported that “due to new laws
in the UK all their books will have to be censored moving forward” to avoid
criminal penalties for “inciting racial hatred.” –The Barnes Review (2020 March/April)
p77 In repressive Germany:
Ursula Haverbeck,
89, Sentenced to 14 Months in Jail for Heresy! –2017 November George Orwell Free Speech Awards:
The Supreme Irony:
□ The Continuing Struggle for Freedom A ray of hope in the ongoing struggle for freedom. Populist and nationalist movements around the world are gaining ascendancy over the New World Order’s effort to establish global governance and impose tyrannical control over every last square meter of the Earth’s surface. –The Barnes Review Vol.23 No.1 (2017 Jan p70)
The ongoing fight for freedom and truth. –Just Right Media (2020, Sept 18, program)
● Pro-Freedom NEWS:
Vanguard News
For more on Freedom (and Objectivism), |
|||
|
... about the author ...
D S S U Research Visits since mid-2010 :
2025-8-22 |
Why Einstein Did Not Receive the Nobel Prize for His Theory of Relativity
|
AbstractWhat follows is an exploration of a number of probable and possible reasons why Einstein did not receive the Nobel Prize for his famous theories on relativity; reasons that include a misinterpreted historic experiment, the prior claims of others, the disturbing lack of causal mechanisms for the phenomena being formulated, the various biases and concerns of the Nobel selection committee, and the incompleteness of the theories. In a most fundamental way relativity was (and is) contrary to the evidence. Relativity is a theory that denies the presence of aether or at least claims it is not detectable; while in the real world positive results of its presence were repeatedly obtained in the form of measurable aether motion. A measurable aether frame-of-reference implies the reality of absolute motion. Einstein denied this reality. Both special and general relativity are therefore incomplete. The weight of evidence seems to indicate that Einstein was not awarded the Nobel for his relativity because of the famous Miller aether-drift experiments. American physicist Dayton Miller, over the course of many years during the first three decades of the 20th century, had accumulated irrefutable evidence of the flow of aether. Equations employing motion with respect to aether-space are introduced.
|
| Contents: |
1. Main-Article Excerpts |
"The expanding universe ranks
among the most startling discoveries made in the twentieth century."
–Cosmology Professor, Edward R. Harrison |
Why Einstein
Did Not
Receive the Nobel
Prize for His
Theory of Relativity
|
|
That they
[relativity theories] are revolutionary there can be no doubt, in so far as
they substitute mathematical symbols as the basis of science and deny that
any concrete experience underlies these symbols, thus replacing an
objective [universe] by a subjective universe.”
|
Ancient "Relative" Motion
Let us go back in time. Way, way, back ... to the 5th century BC. In the Classical period there had been physical philosophers: men such as Parmenides and Zeno, both natives of Elea, a seaport on the western coast of Italy. They had sought for the "physis" or nature of external things, the laws and constituents of the material and measurable world. [2]
Parmenides tried to see the ultimate reality behind natural phenomena —the essentials which lie behind what is observed. But there were also “things” that were not observable, not perceivable; things, nevertheless, that were conceivable. In his simple classification system Parmenides was able to included both observables and non-observables. But it was not a classification between observables and non-observables but rather between “Being” and “non-Being.” He believed that everything can be classified into Being (reality) and non-Being (not reality). Being is changeless, eternal and motionless; non-Being is change, transitoriness, and motion. According to Parmenides motion and change are unreal and merely illusory.[3]
“In the time of Parmenides motion was explained as an illusion: It did not exist.” [4]
The Parmenidean philosophy held that the universe was continuous and unchanging. Obviously Parmenides reached conclusions quite the opposite to those of Heraclitus, to whom flux and change were the true reality, but for a time the motion-as-illusion view exerted a considerable influence.[5]
The great defender of the motion-as-illusion position was Zeno, a friend and follower of Parmenides. He had devised a series of “proofs,” in the form of paradoxes, to show that motion was quite impossible. The most famous “proof” involves a race between Achilles and the tortoise and argues that motion is not what it appears to be.[6]
The argument is that if Achilles and the tortoise run a
handicap race, Achilles can never overtake his competitor. Suppose the tortoise
starts a certain distance down the track, then while Achilles runs up to the
starting point of the tortoise, the latter will have moved somewhat further
ahead. While Achilles runs to this new position, the tortoise again will have
gained a point slightly further on. Every time Achilles closes in on the
tortoise’s previous position, the creature will have crawled away. Achilles does
of course come closer and closer to the tortoise, but he will never catch up
with it.[7]
(See Fig. 1)
|
||
|
Fig. 1. Achilles’ double handicap race. First handicap, the tortoise is given a head start. Second handicap, Achilles is denied the use of absolute motion. Zeno has deemed that Achilles’ motion must be relative to the tortoise but, perversely, always and forever towards the tortoise. Every time Achilles reaches the tortoise’s previous position the creature, as fast as it can slowly advance, has moved out ahead. |
Zeno’s proof uses a peculiar form of relative motion.
Achilles’ position is relative to some in-between point; a moving point which by the defining aspects of the race can never reach the tortoise’s position. And since the motions are not continuous but incremental, Zeno leads us into an infinite regression of infinitely smaller advancements. Achilles and the in-between point, although moving, stay on the trailing side of the tortoise. Achilles, forever finds himself merely catching-up; forever on the losing side.
Notice that Zeno equates subsequent motion to a fraction of the prior motion. He does so recursively, repeatedly, and without end. A truly clever form of relativity. Zeno ignores Achilles’ absolute speed, applies his peculiar relative speed, and ends up with no motion (at least no perceptible motion).
Obviously the paradox arises only if you ignore the fact of absolute motion. Zeno, of course, was wrong because he ignored the absoluteness of motion.
Jumping forward in time and into the 19th century, the concept of absolute motion was long the norm and near the end of that century a working theory of relativity based on absolute motion had been developed. Notably, it worked at all speeds up to the speed of light. Then, at the beginning of the 20th century the modern physical philosopher Albert Einstein (1879-1955) formulated a new theory of relative motion —and, in the spirit of Parmenides and Zeno, he too ignored the absoluteness of motion.
Why Einstein Ignored Absolute Motion
In a famous 1887 experiment, known as the Michelson and Morley aether experiment, it was reported that the speed of the aether wind measured far less than had been expected. Subsequently, others began referring to the Michelson and Morley null result. The experiment was hailed as the death blow to the previously popular aether concept.
Evidently the experiment and the contemporary reaction had an influence on Albert Einstein.
Einstein referred several times to the interferometer experiment, stating that he ‘had thought about the result even in his student days’... that after 1905 he and [Hendrik] Lorentz had discussed the Michelson-Morley experiment many times while he was working on the general theory of relativity. –R. S. Shankland[8]
Years later (in 1931), in a public tribute to Michelson’s extensive contribution to science, Einstein acknowledges the experiment’s influence to his own work:
My honored Dr. Michelson, it was you who led the physicists into new paths, and through your marvelous experimental work paved the way for the development of the theory of relativity.[9]
Einstein must have reasoned that if the aether could not be detected then there could be no way to detect absolute inertial motion. So he abandoned the idea of an absolute frame of reference to which motion could be referenced. Motion could only be referenced to other objects and other observers. In other words motion was relative and nothing more.
As far as Einstein was concerned, there was no aether substance that fills space.
It must be pointed out that a perfectly sound explanation of the smallness of the Michelson-Morley measurements had been developed. In 1891 the Irish physicist George F. FitzGerald explained the ‘null’ result “on the hypothesis that the forces binding the molecules of a solid might be modified by the motion of the solid through the [a]ether in such a way that the dimension of the stone base of the interferometer would be shortened in the direction of motion and that this contraction ... neutralizes the optical effect sought in the Michelson-Morley [aether] experiment.” [10] It was a brilliant hypothesis.
Essentially, FitzGerald’s aether had the relativistic ability to contract the dimensions of any object: contraction occurring in the direction of motion and in proportion to the speed through the aether!
|
The FitzGerald-Lorentz Explanation Historically it has been argued that the motion through the aether shortens the arm (and base) of the Michelson-Morley apparatus in the direction of motion. And this shrinking, now called Lorentz contraction, is just enough to compensate for the calculated longer light path. Consequently, the longer light path is not longer after all and very little, if any, interference shift should be expected. |
Then in 1895, the Dutch physicist, Hendrik A. Lorentz (1853-1928) developed the FitzGerald hypothesis into a sound theory. Given that the atoms of all solids are held together by electrical forces, then the motion of a body as a whole would, according to Clerk Maxwell’s physics, superpose upon the electrostatic forces between the atoms a magnetic effect due to the motion. “There would result a contraction of the body in the direction of motion which is proportional to the square of the ratio of the velocities of translation and of light and which would have a magnitude such as to annul the effect of [a]ether-drift in the Michelson-Morley interferometer.” [11]
The validity of this interpretation, the FitzGerald-Lorentz interpretation, was later confirmed. Whenever the experiment was performed in a vacuum the aether-effect on the optical interferometer was (and still is) totally annulled.
But experimental results were only of secondary importance to Einstein. He was a theoretical physicist —a mathematical physicist. He was a Platonic physicist to whom numbers were more real and important than apparent reality or even objective reality. If you find that strange, then prepare yourself.
It is stranger by far that Einstein would actually ignore the phenomenon that his own theory predicts. His theory of special relativity deals with the speed-of-light constancy, time dilation, mass change, and length contraction! The FitzGerald-Lorentz explanation was essentially a theory of aether-induced length contraction. Einstein, who frequently communicated with Lorentz, most certainly was aware of it. The mathematical physicist rejected the aether-induced length contraction.
Einstein preferred to postulate length contraction, not relative to an aether type of space, but relative to the observer —a relatively moving observer. Now since the degree of apparent length contraction is proportional to the relative speed (between observer and object) it is easy to see that different observers moving with different speeds will measure different length contraction for the same object! I hasten to add, there is nothing wrong with this; special relativity does give a logical explanation. However, special relativity gives no hint as to what the actual length contraction may be. It simply can not. It cannot deal with the absolute length contraction because it has no causal mechanism. These concrete considerations are outside the scope of the theory. That is why it is a theory of relatively moving frames-of-reference, and not a theory of length contraction.
When Einstein turned his back on the aether medium he abandoned not only the phenomenon of absolute motion but he also abandoned all hope of attributing a cause for the length contraction associated with an object’s motion.
What makes all this into a fascinating multilevel puzzle is that, as we now know, Einstein and Lorentz were both right with respect to length contraction. Special relativity can account for apparent contraction while Lorentz’s aether theory can account for absolute contraction.
Einstein rejected the actuality of absolute motion for two main reasons: He misinterpreted the Michelson-Morley results, choosing to believe that absolute motion could not be detected. He sought a purely mathematical theory of motion.
The Aether Evidence and Detection of Absolute Motion
|
How Einstein Won the Nobel In 1902 Philipp Lenard, professor at Kiel, won the Nobel award for the discovery of the photoelectric effect. But he couldn’t explain it. In 1905 the young Einstein gave the correct explanation, and in 1921 won his Nobel for it.[12] The 1921 award honored Einstein only for his light-quanta hypothesis as it explained the photoelectric effect for which Robert Millikan’s experiments already had provided confirmation. The citation read “for discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect, through which quantum theory received a new especially vigorous renewal.” [13] Thus, though Einstein did not win for his renowned relativity theories, he did win the Nobel Prize for what he considered his most revolutionary idea.[14] |
And so, believing absolute motion could not be detected, Einstein confined his arguments to relative motion. But it was not a blind belief; he knew that if absolute motion could be detected then his relativity theory would be wrong.
Einstein fully realized that his theory could not stand if the claimed discovery of aether is ever confirmed (or equivalently, if absolute motion, that is, non-rotational absolute motion, is ever detected). And of particular concern to Einstein were the claims then being made by American physicist Dayton Miller.
In letters written to colleagues he expressed his grave concern.
Einstein stated in a letter, July 1925, to Edwin E. Slosson,
My opinion about Miller's [aether] experiments is the following. ... Should the positive result be confirmed, then the special theory of relativity and with it the general theory of relativity, in its current form, would be invalid. Experimentum summus judex. Only the equivalence of inertia and gravitation would remain, however, they would have to lead to a significantly different theory.[15]
In June of 1921, Einstein wrote to the physicist Robert Millikan:
I believe that I have really found the relationship between gravitation and electricity, assuming that the Miller experiments are based on a fundamental error. Otherwise, the whole relativity theory collapses like a house of cards.[16]
Einstein revealed (privately, at least) the vulnerable conditional component by which his theory could be shaken to its foundations. Centuries earlier, another intellectual giant, René Descartes, did much the same thing when he wrote that if the speed of light could be proved to be finite, his natural philosophy would be “shaken to its foundations” by the findings.
As the chronicles of history record, absolute motion, and therefore aether itself, was detected. It was detected repeatedly.
In 1902 Morley and Miller increased the sensitivity of the Michelson optical interferometer by making the arm length 430 cm (more than three times the length used in the 1887 experiment). The aether drift measured 10 km/s. Their next experiment was in 1904 and saw the first use of the Michelson interferometer mounted on a steel-girder base. Each arm was again 430 cm long. The instrument registered about 7.5 km/s. A year later, in 1905, the same steel-girder apparatus recorded 8.7 km/s. These experiments took place in Cleveland.
In a remarkable 1913 experiment, known as the Sagnac Experiment, it was shown that the aether has a dramatic effect on the speed of light. Using a rotating platform, M. G. Sagnac split light from a single monochromatic source into cw and ccw rays that traveled identical paths in opposite directions around the platform. He combined the returning rays to form a visible interference pattern, and found that the fringes shifted as the speed of rotation changed.
The procedure involved measuring the difference in the travel time of light rays circumnavigating the rotating disk (radius of 25 cm) in opposite directions. The circular path is achieved by the use of mirrors mounted on the disk along the circumference. As in the Michelson-Morley experiment, the time difference was detectable as a fringe shift of the interference pattern of the recombined light beam. Sagnac found, in agreement with prediction, a significant fringe shift. In fact, a rotational speed of 13 m/s produces a full fringe shift.
If the speed of light were locally invariant and always equal to c, then speeding up or slowing of the rotation rate of the platform should not change the location of the fringes. However, the fringes do change with speed and “we can determine a preferred frame —in violation of the second relativity postulate and the hypothesis of locality.” [17]
In April of 1921 Dayton Miller’s steel-girder apparatus was tested on Mt. Wilson, California, and measured an aether flow of 10 km/s.
In Dec of 1921 the steel base was replaced with a concrete one to exclude any possible magnetic effects. Same result, 10 km/s.
Miller’s experiments back in Cleveland during 1922-24: Various apparatus changes and procedural methods were extensively tested. Some improvements were made. Tests of intentional temperature variations in “these experiments proved that under the conditions of actual observation, the periodic displacements could not possibly be produced by temperature effects”[18] as is so often claimed. Throughout the many trials the optical interferometer never failed to produce consistently positive results.
In 1924 Miller again conducted experiments on Mt. Wilson and again measured about 10 km/s.
The years 1925-26 witnessed Miller’s definitive experiments (on Mt. Wilson). While in previous experiments the direction of relative motion between Earth and aether had been assumed, this series of experiments was designed to actually measure the direction. Readings were made throughout 24-hour periods; naturally during the 24-hour rotation of the Earth on its axis there would occur two instances when the fringe shifts became maximum thereby indicating the approximate direction of aether drift (somewhat in the manner by which the ocean tides indicate the direction of the moon). Then, by checking the direction —by repeating the 24-hour test— during different seasons of the Earth’s annual Solar orbit, the experiment establishes whether or not the main component of the aether wind is local or cosmic in origin. A more or less constant direction (in the celestial sphere) indicates a cosmic origin.[19]
Data were collected April 1, August 1, and September 15, 1925, and February 8, 1926. The line of motion was established but there was some uncertainty as to which diametrically opposite direction actually represented the apex of the motion. Eventually Miller concluded that the cosmic direction of motion of the Earth and the Solar System is (Right Ascension ~5h; Declination ~70°S) towards the constellation Dorado. The speed was calculated to be 208 km/s.[20]
Many years later, in a non-optical experiment (performed by Roland DeWitte, in 1991) the Right Ascension direction of ~5h was dramatically confirmed.
During subsequent decades of the 20th century there were several other significant experiments giving positive results.
Then, in the year 2002 the Michelson and Morley data —as well as Miller’s data —were re-analyzed and it became clear for the first time why their measurements of aether drift were so much smaller than had been predicted. The re-analysis, undertaken by Australian Professor Reginald Cahill, actually took the Lorentz contraction into account along with the dielectric nature of the gas (air) affecting the light paths and found that the tangent-to-earth-orbit component of the aether wind matched the predicted 30 km/s.[21]
Absolute motion became an established fact.
What Einstein had feared has come to pass. ... Zeno’s Nemesis finally awoke and dutifully struck another blow against abstract relativity.
... continues ...
No Award for General Relativity
Einstein’s general theory of relativity generalizes special relativity to non-inertial frames of reference. It deals with events occurring in frames of reference that are accelerating due to motion or are accelerating due to gravitation. It is called a geometrodynamic theory. Geometric because, having no aether-type space, it uses a mathematical space defined by four coordinates. Dynamic because its mathematical space curves in accordance with the presence and motion of mass particles and bodies. And what is space curvature? Well, that is one of Einstein’s abstractions. In fact it is an abstraction in geometry borrowed from Georg Friedrich Riemann (1826-66) and Nikolai Lobachevski (1792-1856).
The general relativity theory first appeared in 1915. Because it deals with gravitational acceleration it is called a theory of gravity.
Others, including Lorentz, Poincaré, and Le Sage, had made attempts to formulate a theory of gravitation. They all used an aether medium to communicate the gravity effect. The idea of using a gravitational aether has a long tradition going back to the days of Isaac Newton himself; and even earlier to René Descartes with his large and small vortices of aethereal dust producing what we would call gravitational effects.
Did Einstein use a gravitational aether? ... In 1920 Einstein compared his “gravitational ether” with Lorentz's aether and made it clear that the aether of general relativity has no mechanical properties.
“The ether of the general theory of relativity is a medium which is itself devoid of all mechanical and kinematical qualities, but helps to determine mechanical (and electromagnetic) events. ... the ether of the general theory of relativity is the outcome of the Lorentzian ether, through relativization.” –A. Einstein
Relativization!? ... In plain English, for Einstein, the aether serves no purpose; it is simply ignored, and might as well not exist. Einstein the mathematician gives aether four-dimensional coordinates, discards the aether medium, and retains the coordinates. That procedure is called relativization.
The term symbolized a new vision for a new age. Einstein’s general relativity was the dawn of the age of the mathematical universes. The four-dimensional relativization of the cosmos became a serious enterprise.
In 1916 and into 1917 Einstein developed the very first model of the universe based on the new gravity theory. It was a failure. Although it was designed as a static universe it turned out to be unstable. The instability was pointed out by the Russian mathematician Alexander Friedmann. Gravity and Lambda (a cosmic antigravity effect) were initially balanced but with the slightest disturbance Einstein’s universe will either contract and ultimately collapse into a self-made black hole or, alternately, expand to infinity. Nevertheless, this incipient application set the trend for the science of cosmology for the rest of the century.
Almost all the theoretical models of the universe developed during the 20th century are based, in one way or another, on general relativity. Einstein went on to design other versions of this genre. In 1932 he teamed up with Willem de Sitter and constructed an expanding universe known as the Einstein-deSitter model. It became a textbook standard for comparative big bang models.
However, no award was ever given for general relativity. And no one —not Einstein nor anyone else— ever received an award for a relativized theory of our Universe. The cofounders of the big bang theory of the universe, the Russian physicist George Gamow and his doctoral student Ralph Alpher (publishing in 1946 and 1948 respectively), never made it onto the Nobel list.
There was no Award given for what has been called “the discovery of the expansion of the universe” and rightfully so; for no such discovery was ever made. Edwin Hubble (1889-1953), on whose behalf the claim is often made, did not discover the expansion of the universe —he discovered a redshift versus distance relationship for distant galaxies. The greater the galaxy’s distance, the longer the wavelength of its light. To extrapolate this variation into proof of the expansion of the whole universe is pure speculation. (Nevertheless, when Modern Astrophysics gets its act together, it will belatedly recognize that Edwin Hubble’s rightful claim is for the discovery of the expansion of aether-space!)
There are far too many problems with general relativity models to cover in this article. I will only highlight a few relevant issues. One is that when applied to the universe general relativity is a weak theory. Dennis Sciama describes the problem this way:
“For instance, general relativity, ... is consistent with an infinite number of different possibilities, or models, for the history of the Universe. Needless to say, not more than one of these models can be correct, so that the theory permits possibilities that are not realized in Nature. In other words, it is too wide. We can put this in another way. In the absence of a theory anything can happen. If we introduce a weak theory too many things can still happen.”
There are so many problems with such models that papers are written in an effort to keep track of them: Legendary astronomer Allan Sandage came up with one titled “23 astronomical problems for the next three decades” and was submitted to the conference on Key Problems in Astronomy and Astrophysics (Sandage, 1995). The Russian physicist Yurij V. Baryshev has published the “Conceptual Problems of Fractal Cosmology” which includes several outright paradoxes and in which he concludes “The roots of many of the conceptual problems of modern cosmology ... actually lie in the gravity theory.” And there are web articles; for example, The Top 30 Problems with the Big Bang.
Surely the most embarrassing problem is the inability to explain the observed large scale structure —the network of cosmic voids surrounded by linked galaxy clusters. There is far too much regularity. Furthermore, as plasma physicist and science writer Eric J. Lerner points out, to form these structures by building up the needed motions through gravitational acceleration alone would take in excess of 100 billion years.
How the original unstructured universe evolved into its present highly structured state is a major unsolved riddle in cosmology. –Edward Harrison
In the year 2003 Jaan Einasto reminded the astrophysics community to take note that the big bang models neither predict the position, nor the presence and extent of the regularity of the supercluster-void network (the largest observed structural network in the Universe). The origin of the pattern regularity and the physical scale are unknown.
Then there is the metaphysical nature. General relativity converts time into a special dimension. Time was spatialized and reduced to a timeline by the c constant. But, as we all know, our world only has three dimensions. When you transform time into a fourth dimension, as Einstein did, you are modeling an imaginary mathematical universe, not any kind of real universe. You are placing your theory outside the realm of physics and, in the context of the Nobel Prize, outside the realm of contenders. And doubt not that Einstein constructed an imaginary world, for in order to make time a 4th-dimension coordinate it was necessary to multiply “time” by the factor (√-1) thereby converting time into an imaginary number.
There is also the perennial problem pertaining to cause. The same problem that plagued Newton’s gravity theory also infests Einstein’s gravity —no causal mechanism.
It may never be known for certain whether these unreal aspects and metaphysical ambiguities influenced the Foundation to make policy changes for certain categories. What we do know is that after 1922 the Nobel Prize committee decided, in private, without making the decision public, to exclude discoveries and theories in astrophysics.
Many years later an award was made for an astrophysics finding. Arno Penzias and Robert W. Wilson shared the Award for the “Discovery of cosmic background radiation” —not for finding evidence of a big bang expanding universe. Their 1978 Award was for an observational phenomenon and not for its specific cause and certainly not for any general relativity theory of the universe.
In hindsight the selection committee’s decision to withhold judgment, regardless of motivation, was fortuitous indeed. All general relativity universe models —Hot Big Bang, Cold Big Bang, Steady State, Quasi Steady State, and now the Double Dark model— all treat the universe as a single-cell entity. Each one models the universe as a monolithic mathematical sphere —formulated so that it is only partially visible to us. (Formulated so that no one making a critical assessment of one of these relativity-type models can say Oh! look way over there, one can see the edge of the universe!)
The models of the twentieth century were conceived as single cells. Einstein built the prototype; his legacy to cosmology built the others. However, it turns out that the Universe is actually multi-cellular; intrinsically so; and surprisingly regular.
The eminent physicist Max Planck, who himself had been awarded the Nobel Prize of 1918, nominated Einstein for the 1919 prize, for general relativity, but in vain.
... continues ...
Full 15-page article: Why Einstein Did Not Receive the Nobel Prize for His Theory of Relativity (www.cellularuniverse.org/R6NoNobelForRelativity-Ranzan.pdf) (PDF download)
Reprinted by permission of Physics Essays Publication, from Physics Essays Vol.22, No.4, p564 (2009), DOI:10.4006/1.3252983 (PDF)
References
[1] L. T. More, as in I. Bernard Cohen, Revolution in Science (The Belknap Press of Harvard University Press, Cambridge, Mass., 1985) p414
[2] Will Durant, The Story of Philosophy (Doubleday, Toronto, 1927) p12
[3] Colin Ronan, Science: Its History and Development Among the World Cultures (The Hamlyn Publishing Group Ltd, New York, 1982) p79
[4] Lawrence L. LeShan and Henry Morgenau, Einstein’s Space and Van Gogh’s Sky (Macmillan Publishing Co. New York, 1983) p124
[5] Colin Ronan, Science: Its History and Development Among the World Cultures (The Hamlyn Publishing Group Ltd, New York, 1982) p79
[6] Zeno’s defense of Parmenides’ theory is indirect; his argument is more an attack on the quantization model of the Pythagoreans.
[7] Bertrand Russell, Wisdom of the West, Editor Paul Foulkes (Crescent Books Inc., & Rathbone Books, London, 1978) p 42
[8] R. S. Shankland, Michelson-Morley Experiment, The Encyclopedia of Physics, 3rd Edition, Edited by Robert M. Besancon (Van Nostrand Reinhold Co., New York) p748
[9] From a brief biography of Albert A. Michelson:
http://www.sciences.univ-nantes.fr/sites/jacques_charrier/tp/michelson/michelso.html
[10] Dayton C. Miller, The Ether-Drift Experiment and the Determination of the Absolute Motion of the Earth, Reviews of Modern Physics, Vol.5 July (1933) p207
[11] D. C. Miller, The Ether-Drift Experiment and the Determination of the Absolute Motion of the Earth, Reviews of Modern Physics, Vol.5 July (1933) p207; Miller gives reference to: H.A. Lorentz, Versuch Einer Theorie der Electrischen und Optischen Erscheinungen in Bewegten Körpern (E.J. Brill, Leiden, 1895); Theory of the Electron (B.G. Teubner, Leipzig & Berlin, 1909), p195
[12] Burton Feldman, The Nobel Prize: A History of Genius, Controversy, and Prestige (Arcade Publishing, New York, 2000) p137
[13] Ibid. p147
[14] Ibid. p147
[15] As quoted in: James DeMeo. 2002. Dayton Miller's Ether-Drift Experiments: A Fresh Look. (Posted on www.orgonelab.org/miller.htm)
[16] As quoted in: Ronald W. Clark, Einstein: The Life and Times (The World Publishing Co., NY. 1971) p328
[17] Robert D. Klauber, Toward a Consistent Theory of Relativistic Rotation in Relativity in Rotating Frames (Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, 2004) (arXiv:physics/0404027 v1 6 Apr 2004) p6
[18] D. C. Miller, The Ether-Drift Experiment and the Determination of the Absolute Motion of the Earth (Reviews of Modern Physics, Vol.5 July, 1933) p220
[19] D. C. Miller, The Ether-Drift Experiment and the Determination of the Absolute Motion of the Earth (Reviews of Modern Physics, Vol.5 July, 1933)
[20] Ibid.
[21]
Reginald T.
Cahill, 2002. Absolute Motion and Quantum Gravity.
Posted on http://www.mountainman.com.au/process_physics/index_of_papers.htm;
R. T. Cahill, The Michelson and Morley 1887 Experiment
and the Discovery of Absolute Motion, Progress in Physics,
Vol.3, 25 (October 2005)
-----------------------------------
www.CellularUniverse.org
2. The Reluctant Abandonment of Aether
|
One must understand that practically all the leading physicists at the time believed in the existence of aether but because of the seeming impossibility of its detection (according to the then-popular interpretation of the Michelson & Morley experiment) they all struggled, each in his own way, to break away from aether —and the notion of absolute motion with respect to it. The trend of the early 20th century was to rework existing theories and have them based solely on relative motion. Hence, we have Lorentz researching and defending his aether theory while reluctantly helping to establish a principle of relativity. (With this in mind, the reader should be better able to place Lorentz’s extended quote into proper perspective.) In 1921 Lorentz compared his own efforts with those of Poincaré when he wrote: "I have not established the principle of relativity as rigorously and universally true. Poincaré, on the other hand, has obtained a perfect invariance of the electro-magnetic equations, and he has formulated 'the postulate of relativity', terms which he was the first to employ." –Lorentz (1921) (Notice, Poincaré was the first, but Einstein received the credit. That's odd. ... It seems the popular media were just as unreliable then as they are today.) Nevertheless, Lorentz never relinquished his belief that the aether rest frame was the preferred frame in which clocks measure "real" time and objects possess non-contracted lengths. But if the relativity principle is valid then it would be impossible to find the aether frame by experiment (Lorentz, 1913). And Poincaré’s position was just as ambivalent. In 1901 he denied the existence of aether-type space: “There is no absolute space, and we only conceive of relative motion ; and yet in most cases mechanical facts are enunciated as if there is an absolute space to which they can be referred.” –Poincaré (1901) Yet in 1912 in a paper called "The Quantum Theory", Poincaré ten times referred to the aether, and described light as "luminous vibrations of the ether." The point is, the outcome of the M & M experiment had powerfully influenced both sides of the debate. Aether theorists wavered in the defense of aether theory. Most of them gradually abandoned their cherished preferential frame of reference and so helped to misdirect the course of physics for the following 100 years. –CR (2012) |
3. An Obvious Question
|
The aether medium has been repeatedly detected —originally in 1887, definitively in 1925-26, unexpectedly in 1991, and more recently in 2006— but Einstein's relativity theory has not collapsed! Was Einstein wrong in his dire prediction that the discovery of aether would invalidate his theory? It is a prediction that is still echoing, as in this quote from 2005: "If future experiments were to reveal a non-zero aether drift, then Einstein's relativity would crumble." [1] The obvious question is why didn't Einstein's relativity crumble? There are several reasons. First, Einstein had based his prediction on the possibility of the discovery of the 19th-century aether. Einstein feared the discovery of the classical aether. He knew his theory was vulnerable to the classical aether, because if it existed it would, by definition, be detectable (unlike the rival Lorentzian aether, which was theoretically undetectable). However, that is NOT what the various experiments found. They did not discover the classical aether (nor did they find the Lorentzian aether). Second, special relativity has proven to be a highly successful theory for apparent situations —situations with purely relative reference frames. And the vast majority of applications are relative ones. It is only rarely that "absolute" situations arise (and it is only those that lead to paradoxes). Third, whenever practitioners of relativity theory find it necessary or convenient, one of the key elements of the theory is simply ignored. Remember the no-preferred-reference-frame requirement (the abolition-of-aether clause)? ... Well, it has been seriously diluted in meaning; sometimes it is just abandoned. The various "twins" paradoxes are excellent examples. They are not resolvable unless you break the rule and implement a preferred frame. Fourth, the theory received the backing of the establishment, became institutionalized, became a symbol of a new intellectual mystique, and attracted a formidable following. It became a vested interest. In short, Einstein's relativity survives because (i) it can easily be extended [2] to work with an aether frame; (ii) it does agree with many observed phenomena; (iii) it cheats on one of its postulates; and (iv) it has tenacious defenders. Oh yes, there is another reason. I was so buried in the technical details that I had almost forgotten about human nature? ... In order to make meaningful changes to relativity, and move beyond the limitations of Einstein's version, physicists will have to admit that they and their profession got it wrong for 101 years —the years from the historic rejection of aether in 1905 to the third major rediscovery of aether in 2006. ... Such an admission is unlikely to happen. Meanwhile, the paradoxes and inconsistencies remain. –CR (2012) References1. Diana Buchwald and Kip S. Thorne, The Born-Einstein Letters (publisher, Palgrave, USA, 2005) Preface 2. C. Ranzan, Extended Relativity –Exploiting the Loopholes in Einstein's Relativity, Physics Essays Vol.25, No.3, pp327-346 (2012) |
4. More on Zeno's Paradox
Both Zeno and Einstein applied uncompromising
logic to their respective theories of motion.
Zeno applied his logic to a misconception of infinity ; Einstein
applied his to a misconception of space.
In case you are wondering about the resolution of the
famous paradox ...
The mathematical resolution involves showing that an infinite series of
numbers can add up to a finite number.
|
Zeno's Paradox may be rephrased as follows. Suppose I wish to cross the room. First, of course, I must cover half the distance. Then, I must cover half the remaining distance. Then, I must cover half the remaining distance. Then I must cover half the remaining distance . . . and so on forever. The consequence is that I can never get to the other side of the room. What this actually does is to make all motion impossible, for before I can cover half the distance I must cover half of half the distance, and before I can do that I must cover half of half of half of the distance, and so on, so that in reality I can never move any distance at all, because doing so involves moving an infinite number of small intermediate distances first. Now, since motion obviously is possible, the question arises, what is wrong with Zeno? What is the "flaw in the logic?" If you are giving the matter your full attention, it should begin to make you squirm a bit, for on its face the logic of the situation seems unassailable. You shouldn't be able to cross the room, and the Tortoise should win the race! Yet we know better. Hmm. Rather than tackle Zeno head-on, let us pause to notice something remarkable. Suppose we take Zeno's Paradox at face value for the moment, and agree with him that before I can walk a mile I must first walk a half-mile. And before I can walk the remaining half-mile I must first cover half of it, that is, a quarter-mile, and then an eighth-mile, and then a sixteenth-mile, and then a thirty-secondth-mile, and so on. Well, suppose I could cover all these infinite number of small distances, how far should I have walked? One mile! In other words, ... At first this may seem impossible: adding up an infinite number of positive distances should give an infinite distance for the sum. But it doesn't – in this case it gives a finite sum; indeed, all these distances add up to 1! A little reflection will reveal that this isn't so strange after all: if I can divide up a finite distance into an infinite number of small distances, then adding all those distances together should just give me back the finite distance I started with. (An infinite sum such as the one above is known in mathematics as an infinite series, and when such a sum adds up to a finite number we say that the series is summable.) Now the resolution to Zeno's Paradox is easy. Obviously, it will take me some fixed time to cross half the distance to the other side of the room, say 2 seconds. How long will it take to cross half the remaining distance? Half as long – only 1 second. Covering half of the remaining distance (an eighth of the total) will take only half a second. And so one. And once I have covered all the infinitely many sub-distances and added up all the time it took to traverse them? Only 4 seconds, and here I am, on the other side of the room after all. And poor old Achilles would have won his race. – Source: www.mathacademy.com (2009 July) |
5. Historical Note on Einstein and the Nobel Award
|
The following, by Kevin Brown, is from a web-article at www.mathpages.com/home/kmath627/kmath627.htm : The story of how Einstein did not get the Nobel prize in 1920, or in 1921, and the famous reports of Arrhenius and Gullstrand downplaying or disparaging relativity, has been much discussed in the literature, but I’ve never seen any discussion of the (admittedly indirect) connection between Einstein and Guillaume, the man who was awarded the 1920 prize. Gullstrand (a member of the Nobel committee) was quoted as saying that “Einstein must never win the Nobel prize for relativity!”, because he was strongly opposed to what he regarded as the overly abstract and mathematical approach to physics. Both Arrhenius and Gullstrand were obviously acquainted with the relativity literature, especially the literature critical of the theory, so it seems plausible that they were familiar with the “other” Guillaume’s battle with Einstein. Is it purely coincidental that the prize, so pointedly denied to Einstein for relativity theory, was awarded (more or less out of the blue) to the cousin of one of the most vocal critics of relativity theory? … In 1921, the year after Guillaume was awarded the Nobel prize, Einstein was again nominated by many of the world’s leading physicists. Eddington wrote to the committee that “Einstein stands above his contemporaries even as Newton did.” But this is the year in which Gullstrand issued his disparaging report, and the committee decided not to award a physics prize for 1921. The following year, however, the tide had turned. One nominator (Brillouin) asked the committee to “imagine for a moment what the general opinion will be fifty years from now if the name Einstein does not appear on the list of Nobel laureates.” So, in 1922, Einstein was retro-actively awarded the 1921 prize (and Bohr got the 1922 prize). Nevertheless, relativity theory was still seen as too controversial – and too unconnected to the practical world – to be the subject of a Nobel prize. Instead, the committee cited Einstein’s “services to theoretical physics and especially his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect”. It’s worth noting that the award was not for the theory of light quanta, but rather for discovering the “law” of the photoelectric effect. This again reflects the committee’s reluctance to endorse theoretical ideas. Years later when Einstein was asked to list the main awards he had received during his lifetime, he omitted the Nobel prize. The back-to-back Nobel prizes awarded to Guillaume and Einstein exemplifies an interesting fundamental dichotomy. Guillaume’s achievement has often been characterized as “routine” by the community of theoretical physicists, some of whom suggested that it wasn’t deserving of the Nobel – and yet it must be admitted that none of those theoreticians predicted the existence of anomalous behavior (the Invar effect) in metals. [“Invar,” an abbreviation of invariable, is the trademark name of an alloy of iron and nickel with a negligible coefficient of expansion, and is used in the making of clocks and scientific instruments. –C.R.] It was found only by Guillaume’s determined and practical-minded experimentation, and the practical benefits of his discovery have been immense. On the other hand, although Einstein and his theories of relativity were (and still are) revered by theoretical physicists, a good case could be made, at least for general relativity, that the direct practical benefits have been almost non-existent. It’s true that special relativity is fundamental to all of modern physics, to the extent that it’s hard to imagine modern physics without it, but in historical terms the special theory was, as Einstein himself said, “ripe for discovery in 1905”. (Needless to say, the splitting of the atom and the production of atomic bombs was primarily a product of the study of x-rays, radioactivity, and sub-atomic particles by people like Roentgen, Curie, and their successors, rather than a result of special relativity.) Whether quantum mechanics would have been hindered by the absence of the Einstein’s unique elucidation of the principles of special relativity is impossible to say. But it’s easy to see how his work on the photoelectric effect (which ironically was based on the experimental work of Philipp Lenard, another Nobel prize winner and charter member of the Anti-Relativity Company Ltd.), together with his other work related to the light quanta, stimulated emission of radiation, and Einstein-Bose statistics, has been profoundly influential and facilitated the development of important technologies, including both television and the laser, with all the associated applications. Einstein’s theoretical work on relativity is comparable to the heliocentric theory of Copernicus, in the sense that the Copernican model did not lead directly to any practical benefits, and yet it stimulated and facilitated the entire scientific revolution. How then do we measure the “utility” of such fundamental theoretical ideas? Of course, even aside from utility, deep scientific truths possess a beauty that makes them highly valued by anyone with an appreciation for such things, but nothing needs to be said about that. Oddly enough, the two Guillaume cousins seem to have almost merged into a single individual in the scholarly literature. For example, in A. I. Miller’s book on the emergence of special relativity he cites “Charles Edouard Guillaume” as the author of the preface to the 1924 edition of Poincaré’s “The New Mechanics”, in which the case is made for Poincaré’s priority over Einstein, and for the Lorentz/Poincaré ether-based approach. I’m fairly certain that this was actually written by Edouard Guillaume, the Swiss patent examiner who published so many anti-relativity papers, not by his cousin Charles Edouard Guillaume, the discoverer of Invar and winner of the Nobel prize. – Source: http://www.mathpages.com/home/kmath627/kmath627.htm (2014-11-6) |
6. Table-4 Erratum, and a Further Point of Interest
|
For Table 4 (in the Physics
Essays published version).
As a point of interest, although an aether theory is used to derive the above equation, it can easily be verified by taking the relative-to-absolute conversion expression,
and substituting it into the conventional Einstein expression for relativistic momentum:
The result is the DSSU relativistic momentum:
which is just the expanded version of eqn (1) above. DSSU relativity can be thought of as an extension of Einstein's relativity. There exists a mathematical link between the two whereby "relativity" equations can be converted to "absolute" (aether-referenced) equations. This means that any relativity expression such as eqn (3), which contains a pure relative velocity v, can be converted to an absolute expression, eqn (4) in this case, which contains strictly aether-referenced velocities. (Velocities vA and vB are absolute in the sense that they are referenced to the aether medium.) It may not be immediately obvious, but Einstein's eqn (3) and DSSU eqn (4) both give the same answer in any particular situation. –CR |
2015-12
|


.jpg)

.jpg)

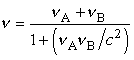 ,
,
 .
(3)
.
(3)